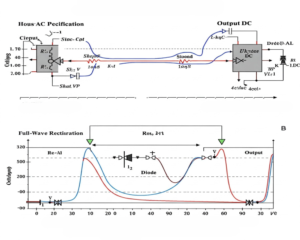
Ever wondered how your phone charger works? A DC power supply converts AC to stable DC voltage. Let’s break down its core parts to understand how it powers your devices.
A basic DC power supply has four key components: transformer, rectifier, filter, and regulator. The transformer adjusts voltage, the rectifier converts AC to DC, the filter smoothens ripples, and the regulator ensures stable output (max 50 words).
Now, let’s explore each component in detail. Knowing these will help you troubleshoot issues or design your power supply.
What Does a Transformer Do in a DC Power Supply?
Transformers are the first step in power conversion. They handle high voltages safely. But how exactly do they work?
Transformers step up or step down AC voltage using electromagnetic induction. They isolate the circuit from the mains voltage, enhancing safety and enabling efficient power transfer (max 50 words).
How Transformers Adjust Voltage
Transformers consist of two coils: primary (input) and secondary (output). The voltage change depends on the turns ratio:
| Turns Ratio (Primary: Secondary) | Voltage Change |
|---|---|
| 1:2 | Step-up |
| 2:1 | Step-down |
Key Features of Power Supply Transformers
- Isolation: Prevents direct contact with high-voltage mains.
- Efficiency: Loses minimal energy as heat.
- Frequency Dependency: Designed for specific AC frequencies (e.g., 50Hz or 60Hz).
Without a transformer, your power supply couldn’t safely handle household AC voltages.
Why Is a Rectifier Essential for DC Conversion?
AC power can’t run most electronics. Rectifiers bridge this gap. But how do they turn alternating current into direct current?
Rectifiers use diodes to convert AC to pulsating DC. Half-wave rectifiers use one diode, while full-wave (bridge) rectifiers use four for smoother output (max 50 words).
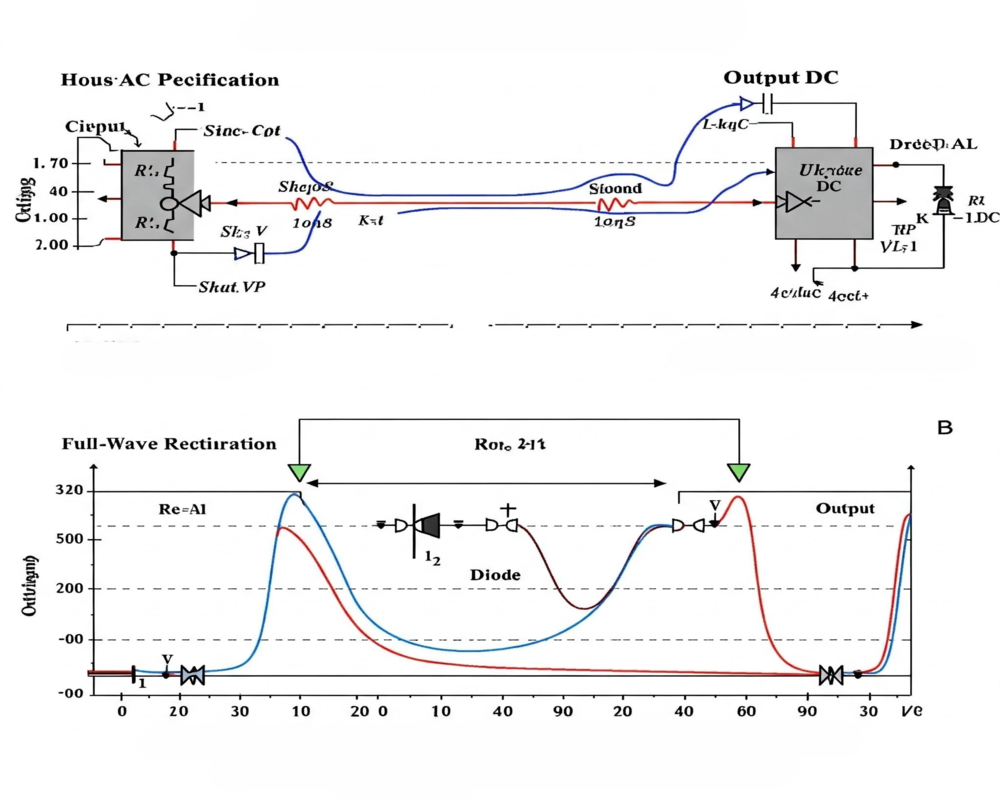
Types of Rectifiers
- Half-Wave Rectifier
- Pros: Simple, low-cost.
- Cons: Wastes 50% of AC input.
- Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier
- Pros: Utilizes both AC phases, doubling efficiency.
- Cons: Requires more diodes (4 vs. 1).
Common Issues
- Voltage Drop: Each diode loses ~0.7V.
- Heat Dissipation: Diodes need heat sinks for high-current applications.
A rectifier’s output is still imperfect—this is where filters come in.
How Does a Filter Stabilize DC Output?
Rectified DC is noisy and unstable. Filters clean this up. But what’s inside a filter, and how does it work?
Filters use capacitors (and sometimes inductors) to smooth ripples. Capacitors store charge during peaks and release it during drops, flattening the output (max 50 words).
Filter Components
- Capacitors:
- Electrolytic capacitors handle high capacitance (e.g., 1000µF).
- Smaller ceramic capacitors filter high-frequency noise.
- Inductors (in LC filters):
- Block AC ripples while allowing DC to pass.
Ripple Voltage Calculation
Ripple (%) = (V_ripple / V_dc) × 100
For example, a 12V DC with 0.6V ripple has 5% ripple. Lower is better for sensitive electronics.
What Role Does a Voltage Regulator Play?
Even filtered DC can fluctuate with load changes. Regulators fix this. But how do they maintain a steady voltage?
Voltage regulators (like LM7805) maintain constant output despite input or load variations. They use feedback circuits to adjust voltage dynamically (max 50 words).
Types of Regulators
- Linear Regulators
- Pros: Low noise, simple design.
- Cons: Waste excess voltage as heat.
- Switching Regulators
- Pros: High efficiency (up to 95%).
- Cons: Complex, expensive.
Key Specifications
- Dropout Voltage: Minimum input-output difference (e.g., 2V for LM7805).
- Load Regulation: Maintains voltage under current changes (e.g., ±1%).
Regulators ensure your device gets clean, stable power—even during sudden power surges.
Conclusion
A DC power supply relies on four core parts: a transformer, rectifier, filter, and regulator. Each plays a vital role in converting and stabilizing power for your devices.